In this article we look at the Arduino Nano, another classic board
This is a much smaller board coming in at 18 x 45 mm versus 68.6 x 53.4 mm so is useful for projects that require a smaller footprint than the Uno
There are a wide range of libraries for sensors and modules available, if you want to use these they can save a great amount of development time. Of course you don’t have to use them.
As well as that there is a huge range of tutorials, code examples and help online – generally all of the examples for the Arduino Uno should work with this board as well.
You get an extra 2 analog pins which may be useful
Existing Arduino Uno shields will not work, I have seen adaptor boards that you can fit a nano in but it doesn’t appear they would allow Uno shields to work but there may be an option out there – cannot rule it out but that would be an extra cost.
Features
The ATmega328 has 32 KB, (also with 2 KB used for the bootloader. The ATmega328 has 2 KB of SRAM and 1 KB of EEPROM.
| Microcontroller | ATmega328 |
| Architecture | AVR |
| Operating Voltage | 5 V |
| Flash Memory | 32 KB of which 2 KB used by bootloader |
| SRAM | 2 KB |
| Clock Speed | 16 MHz |
| Analog I/O Pins | 8 |
| EEPROM | 1 KB |
| DC Current per I/O Pins | 40 mA (I/O Pins) |
| Input Voltage | 7-12 V |
| Digital I/O Pins | 22 |
| PWM Output | 6 |
| Power Consumption | 19 mA |
Pins
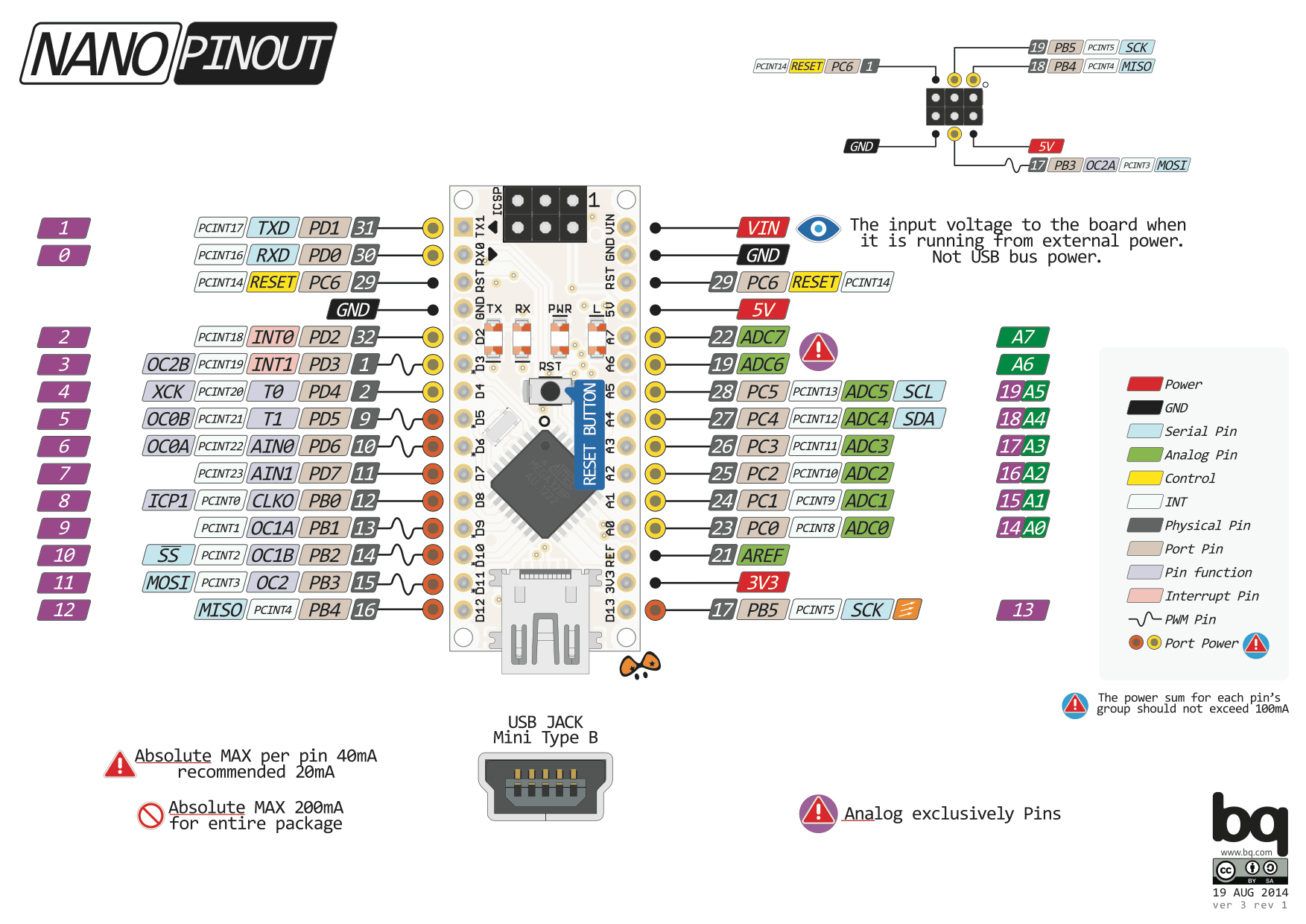
Each of the 14 digital pins on the Arduino Nano can be used as an input or output. They are all 5 volt tolerant. A maximum of 40mA is the value that must not be exceeded to avoid damaging the microcontroller.
The Arduino Uno has 6 analog inputs, each of which provide 10 bits of resolution. By default they measure from ground to 5 volts, though is it possible to change the upper end of their range using the AREF pin.
Serial: 0 (RX) and 1 (TX). Used to receive (RX) and transmit (TX) TTL serial data.
External Interrupts: 2 and 3. These pins can be configured to trigger an interrupt on a low value, a rising or falling edge, or a change in value.
PWM: 3, 5, 6, 9, 10, and 11. Provide 8-bit PWM output.
SPI: 10 (SS), 11 (MOSI), 12 (MISO), 13 (SCK). These pins support SPI communication using the SPI library.
LED: 13. There is a built-in LED driven by digital pin 13. When the pin is HIGH value, the LED is on, when the pin is LOW, it’s off.
The Nano has 8 analog inputs, each of which provide 10 bits of resolution. By default they measure from ground to 5 volts, though is it possible to change the upper end of their range using the analogReference() function. Analog pins 6 and 7 cannot be used as digital pins.
TWI/I2C: A4 or SDA pin and A5 or SCL pin.
AREF. Reference voltage for the analog inputs.
Reset. Bring this line LOW to reset the microcontroller. Typically used to add a reset button to shields which block the one on the board.
Here is a pinout of the board
Installation
The board works out the box with the desktop IDE and the online IDE.
Many examples online
Cost
The price varies wildly on these boards – these are all clone options and all affiliate links.
Some of these are packs of 3
| Site | Link | Price |
| Amazon.com | Nano V3.0, Nano Board ATmega328P 5V 16M Micro-Controller Board Compatible with Arduino IDE (Nano x 3 with USB Cable) | $15.99 |
| Aliexpress | 1PCS arduino Nano | $0.62 |
| Amazon.co.uk | ELEGOO Nano Board 340/ATmega Nano328P compatible with offical Nano (pack of 3) | £10 |
Summary
A small form factor Arduino board with an extra 2 analog pins, again a low cost board with many resources available.
